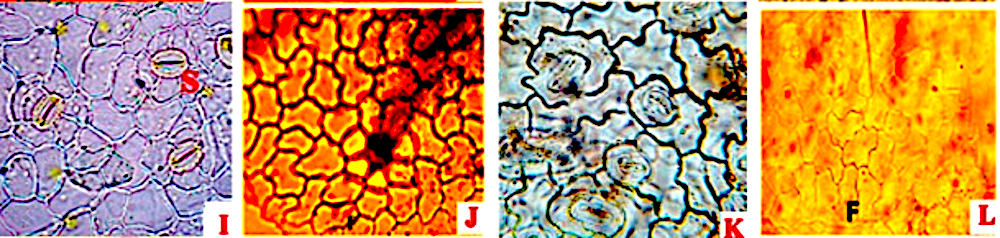
Comparative Pharmacognostic Evaluation of Munronia Pinnata (Wall.) Theob. (Meliaceae) and Its Substitute Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. Ex Nees (Acanthaceae)
by Dharmadasa R. M., Samarasinghe K., Adhihetty P., Hettiarachchi P. L. (2013)
Dharmadasa R.M.1,, Samarasinghe K1, Adhihetty P1, Hettiarachchi P.L2
1Herbal Technology Section, Industrial Technology Institute, Bauddhaloka Mawatha, Sri Lanka
2Rajarata University of Sri Lanka, Mihintale, Sri Lanka
===
In World Journal of Agricultural Research 1 (5): 77-81 –
DOI: 10.12691/wjar-1-5-1 – http://pubs.sciepub.com/wjar/1/5/1/index.html
Stomata


You must be logged in to post a comment.